PlatON WASM合约开发(四)—— 详解参数传递
概述#
PlatON WASM智能合约是支持PlatON隐私计算基础设施用于生态开发的有效工具,在前面的文章中,我们对《合约开发入门》、《跨合约调用》、《事件机制》进行了讲解,本次我们将对合约调用的参数机制进行详细的解读。
合约#
用于测试的wasm合约源文件如下:
#include <platon/platon.hpp>#include <string>#include <vector>#include <list>#include <map>
class inputParams{public: inputParams(){} inputParams(std::vector<int>& vParams){ myParams = vParams; } public: std::vector<int> myParams; PLATON_SERIALIZE(inputParams, (myParams))};
CONTRACT initTest: public platon::Contract{public: ACTION void init(const inputParams& ipa, std::string& myString, int myInt, std::vector<int>& myVec, std::list<std::string>& myList, std::map<int, std::string>& myMap){ _iParams.self() = ipa; _myString.self() = myString; _myInt.self() = myInt; _myVec.self() = myVec; _myList.self() = myList; _myMap.self() = myMap; }
ACTION void setValue(const inputParams& ipa, std::string& myString, int myInt, std::vector<int>& myVec, std::list<std::string>& myList, std::map<int, std::string>& myMap){ _iParams.self() = ipa; _myString.self() = myString; _myInt.self() = myInt; _myVec.self() = myVec; _myList.self() = myList; _myMap.self() = myMap; }
CONST std::vector<int> GetParams(){ return _iParams.self().myParams; }
CONST std::string GetString(){ return _myString.self(); }
CONST int GetInt(){ return _myInt.self(); }
CONST std::vector<int> GetVec(){ return _myVec.self(); }
CONST std::list<std::string> GetList(){ return _myList.self(); }
CONST std::map<int, std::string> GetMap(){ return _myMap.self(); }
private: platon::StorageType<"Params"_n, inputParams> _iParams; platon::StorageType<"string"_n, std::string> _myString; platon::StorageType<"int"_n, int> _myInt; platon::StorageType<"vector"_n, std::vector<int>> _myVec; platon::StorageType<"list"_n, std::list<std::string>> _myList; platon::StorageType<"map"_n, std::map<int, std::string>> _myMap;};
PLATON_DISPATCH(initTest, (init)(setValue)(GetParams)(GetString)(GetInt)(GetVec)(GetList)(GetMap))该合约设计的init接口,能够较为全面覆盖各类参数的情况,主要包括:
- 自定义对象型参数(inputParams);
- std::string型参数;
- int型参数;
std::vector<...>型参数;std:list<...>型参数;std::map<..., ...>型参数。
部署时初始化输入参数的形式#
当通过platon-truffle部署调用init时,输入参数的表现形式如下:
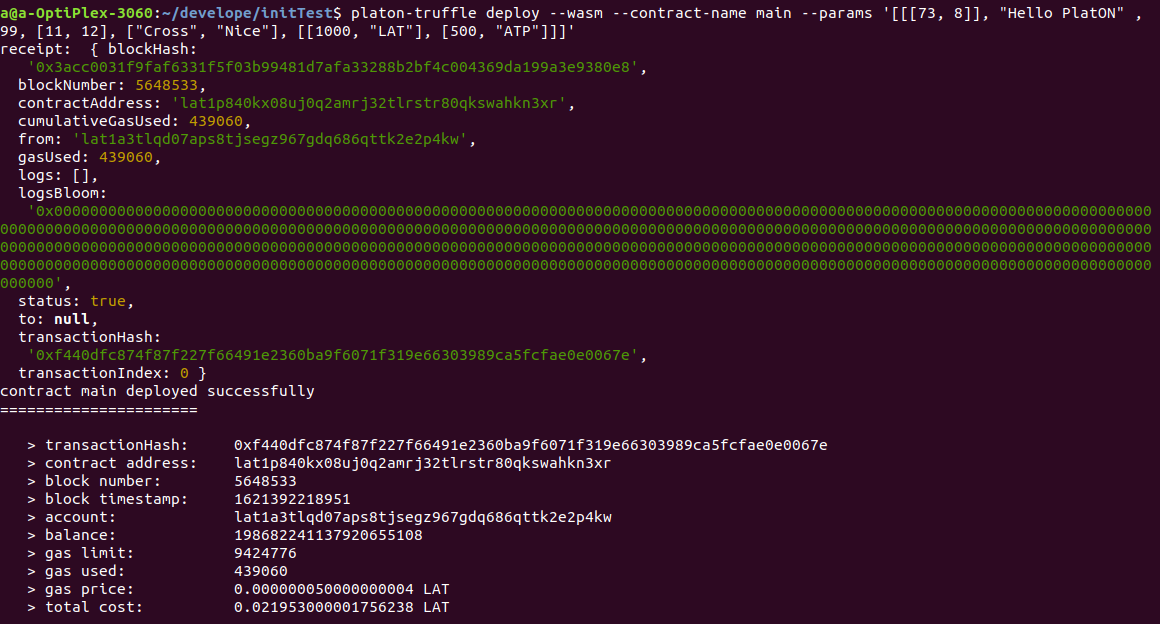
部署成功会出现类似上图的输出。
完整部署命令为:
platon-truffle deploy --wasm --contract-name main --params '[[[73, 8]], "Hello PlatON" , 99, [11, 12], ["Cross", "Nice"], [[1000, "LAT"], [500, "ATP"]]]'输入参数为--params后面的内容:
'[[[73, 8]], "Hello PlatON" , 99, [11, 12], ["Cross", "Nice"], [[1000, "LAT"], [500, "ATP"]]]'其中:
- 最外层[],代表多个参数需要以列表的形式进行传递;
- 列表中的参数顺序与接口形参的顺序一致;
- [[73, 8]],对应参数const inputParams&,其表现形式为[[int, int, int,...]],外层[]代表输入的是一个自定义类对象,而该对象的初始化需要
std::vector<int>&作为构造参数,因此内层也是一个int列表[73, 8]; - "Hello PlatON"对应参数std::string&;
- 99对应参数int;
- [11, 12]对应参数
std::vector<int>&; - ["Cross", "Nice"]对应参数
std::list<std::string>&,可以看到,std::vector<...>、std::list<...>型参数,都是对应的[..., ..., ...]这样的形式; - [[1000, "LAT"], [500, "ATP"]]对应参数
std::map<int, std::string>&。std::map<...>型参数没有采用json中比较直观的{key: value}格式,选择了使用
[[key1, value1], [key2, value2],...]这样的形式,采用这种方式的一种考虑是,json的{key: value}类型对key有类型限制。
调用接口验证初始化结果#
platon-truffle console里面调用接口的准备工作如下(详见《合约开发入门》):
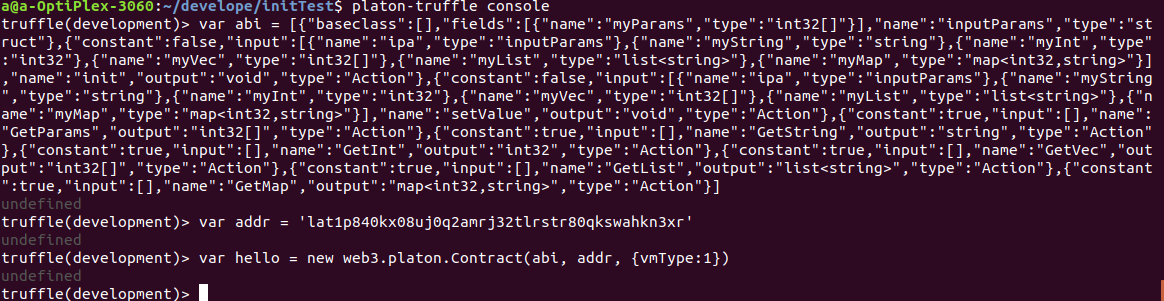
调用各种类型的Get接口,查看各个类型的值:
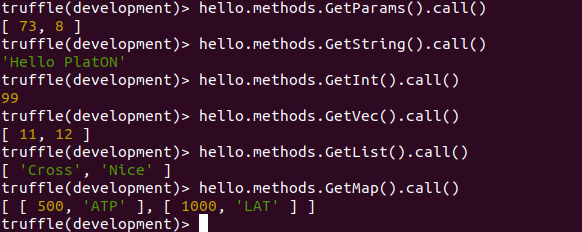
返回值与部署时传递的参数值一致。
调用普通接口的参数传递方式#
调用命令为:
truffle(development)> hello.methods.setValue([[733, 88]], "Great PlatON" , 999, [111, 122], ["Hello", "Cross"], [[10000, "LAT"], [5000, "ATP"]]).send({from:'lat1a3tlqd07aps8tjsegz967gdq686qttk2e2p4kw', gas:999999})普通接口的调用与一般的函数调用类似,唯一需要注意的只是对于map型参数,依然需要采用以下形式:
[[key1, value1], [key2, value2]]调用成功输出:
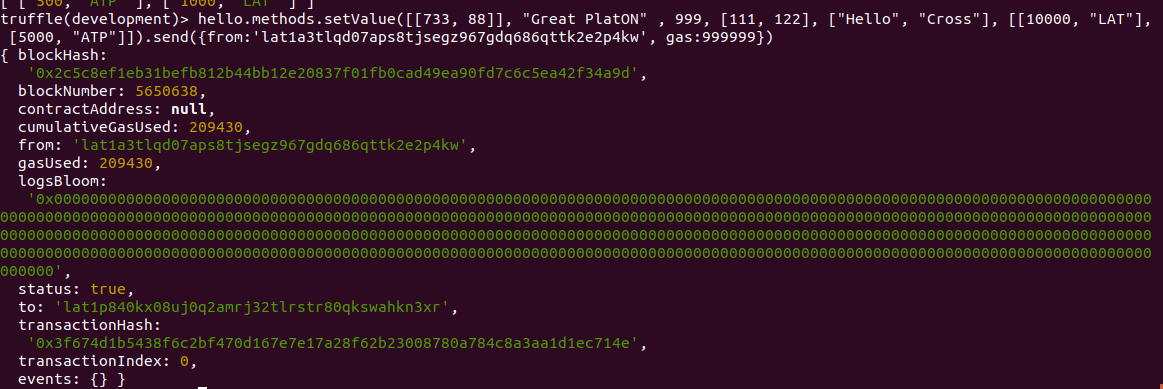
调用各种类型的Get接口,获取各种类型的值如下:
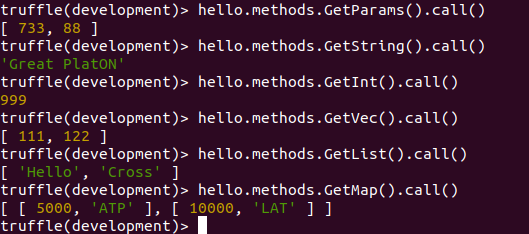
总结#
根据以上案例分析,对参数传入规则总结如下:
- 对于使用platon-truffle部署时调用的初始化接口(init),参数以json列表形式进行传递,列表中各个信息应按照接口参数顺序排列;
- 对于普通接口调用,直接按函数调用的类似方法传递参数;
- 对于
std::vector<...>、std::list<...>型参数,以列表形式传递参数; - 对于
std::map<..., ...>型,以[[key1, value1], [key2, value2],...]形式传递参数; - 对于自定义对象型参数,以列表[...]形式传递,列表中元素为对象初始化所需要的参数。
本教程贡献者 @xiyu