PlatON WASM contract (五) - 代理机制
概述#
从本篇开始,Cross技术团队将开始对PlatON上WASM智能合约的一些进阶使用进行讲解。 经编译部署后的区块链智能合约本质上是记录在链上的一段字节码,因为区块链不可篡改的特点,合约部署后实际上是“永远”保存在了链上,而智能合约作为DApp的“后台”,在使用过程中,由于应用功能的迭代更新,其更改迭代的需求几乎是必然的。目前,PlatON上的WASM合约尚未公开直接进行合约在线更新的底层机制,本篇内容将提供一种可应用于PlatON上WASM智能合约在线升级的代理机制,有关合约在线升级其他方面的内容,将在后续文章中进行讲解。
示例说明#
本文示例由三个合约组成:contractProxy(代理合约)、calcContract(业务合约1)、calcContract2(业务合约2)组成。
contractProxy#
contractProxy合约的功能分为两部分:一是完成代理管理的相关功能,二是对业务接口的调用,合约代码如下:
#include <platon/platon.hpp>#include <string>
//this proxy instance can be proxy for only one contract at a time//real contract shall be deployed before this proxy is deployedCONTRACT calc_contract_proxy : platon::Contract{public: PLATON_EVENT1(incalcAdd, std::string, int) PLATON_EVENT1(inmakeSum, std::string, int)
//the input param is for Security considerations ACTION void init(std::string& contractAddr){ auto rst = platon::make_address(contractAddr); //when the contractAddr is illegal, the proxy can not be used if (!rst.second){ platon::internal::platon_throw("deploy failed!"); } else{ _contractAddr.self() = rst; } }
//contract can be altered. But the caller must be current contract ACTION bool RegisterContract(std::string& contractAddr){ //can't be called when owner is illegal if (!_contractAddr.self().second){ platon::internal::platon_throw("this contract init failed!"); return false; }
platon::Address senderAddr = platon::platon_caller();
//if caller is the owner, replace the owner address if (senderAddr != _contractAddr.self().first){ return false; }
auto result = platon::make_address(contractAddr); if (!result.second){ return false; }
_contractAddr.self() = result; return true; }
//the following methods are for represented contracts //the interfaces are agree with the represented contracts ACTION std::pair<int, bool> calcAdd(int a, int b){ //can't be called when owner is illegal if (!(_contractAddr.self().second)){ platon::internal::platon_throw("this contract init failed!"); return std::pair<int, bool>(0, false); }
//make call to real contract auto result = platon::platon_call_with_return_value<int>(_contractAddr.self().first, (unsigned int)(0), (unsigned int)(0), "calcAdd", a, b); PLATON_EMIT_EVENT1(incalcAdd, "calcAdd" , result.first); return result; }
CONST std::pair<int, bool> const_calcAdd(int a, int b){ //can't be called when owner is illegal if (!(_contractAddr.self().second)){ platon::internal::platon_throw("this contract init failed!"); return std::pair<int, bool>(0, false); }
//make call to real contract auto result = platon::platon_call_with_return_value<int>(_contractAddr.self().first, (unsigned int)(0), (unsigned int)(0), "const_calcAdd", a, b); return result; }
ACTION std::pair<int, bool> makeSum(std::vector<int>& eles){ //can't be called when owner is illegal if (!(_contractAddr.self().second)){ platon::internal::platon_throw("this contract init failed!"); return std::pair<int, bool>(0, false); }
//make call to real contract unsigned int len = eles.size(); if (0 == len){ PLATON_EMIT_EVENT1(inmakeSum, "makeSum" , 0); return std::pair<int, bool>(0, true); } else{ //call methods auto result = platon::platon_call_with_return_value<int>(_contractAddr.self().first, (unsigned int)(0), (unsigned int)(0), "makeSum", eles); PLATON_EMIT_EVENT1(inmakeSum, "makeSum" , result.first); return result; } }
private: platon::StorageType<"contract"_n, std::pair<platon::Address, bool>> _contractAddr;};PLATON_DISPATCH(calc_contract_proxy, (init)(RegisterContract)(calcAdd)(const_calcAdd)(makeSum))接口说明:#
- init:初始化,部署时调用,需要输入正常的lat地址(最好是业务合约,也可以是普通地址);
- 代理管理相关接口:
- RegisterContract:更改业务合约地址时调用,调用者必须是当前地址的拥有者;
- 业务代理调用接口:
- calcAdd、const_calcAdd、makeSum,通过调用真实的业务合约接口,完成业务操作,获取执行结果,并通过事件机制返回业务执行结果;
- 说明:在本文案例中,代理合约中的业务代理接口,需要与业务合约中的相关接口一致,实际上,可以开发更加通用的方式,例如将业务合约接口的代理调用封装到一个可变参数的接口中完成。
业务合约1(calcContract)#
业务合约1完成实际的业务操作,同时也需要实现一定的代理管理操作功能。从业务合约1的代码可以看到 ,作为被代理合约,在实现缺少必要的保护机制。合约代码如下:
#include <platon/platon.hpp>#include <string>#include <vector>
CONTRACT calc_contract : public platon::Contract{public: ACTION void init(){ //the owner of the contract is best to be the operator of the deployment //in this instance, owner address can not be changed _ownerAddr.self() = std::pair<platon::Address, bool>(platon::platon_caller(), true); }
//methods for proxy mechanism //this methods shall be called only after the proxy contract is deployed ACTION bool RegisterProxy(const std::string& proxyAddr){ //set and register the proxy address auto p_Addr = platon::make_address(proxyAddr); if (!p_Addr.second){ _proxyAddr.self() = std::pair<platon::Address, bool>(platon::Address(), false); platon::internal::platon_throw("register proxy failed! illegal proxy address!"); return false; } else{ _proxyAddr.self() = p_Addr; return true; } }
CONST std::string GetProxyAddress(){ return _proxyAddr.self().first.toString(); }
CONST std::string GetOwnerAddress(){ return _ownerAddr.self().first.toString(); }
//the param is the next contract address the proxy really use ACTION bool updateContract(const std::string& contractAddr){ //only owner can updateContract auto send_Addr = platon::platon_caller(); if (_ownerAddr.self().first != send_Addr){ return false; }
//check the contract address auto c_Addr = platon::make_address(contractAddr); if (!c_Addr.second){ return false; }
//call proxy if (!_proxyAddr.self().second){ return false; }
auto result = platon::platon_call_with_return_value<bool>(_proxyAddr.self().first, (unsigned int)(0), (unsigned int)(0), "RegisterOwner", contractAddr); return result.second; }
//calculation methods ACTION int calcAdd(int a, int b){ return a + b; }
CONST int const_calcAdd(int a, int b){ return a + b; }
ACTION int makeSum(std::vector<int>& eles){ int rst = 0; for (auto itr = eles.begin(); itr != eles.end(); ++itr){ rst += *itr; } return rst; }
private: //contracts using proxy mechanism are needed to using owner address principle. platon::StorageType<"owner"_n, std::pair<platon::Address, bool>> _ownerAddr; platon::StorageType<"proxy"_n, std::pair<platon::Address, bool>> _proxyAddr;};
PLATON_DISPATCH(calc_contract, (init)(RegisterProxy)(GetProxyAddress)(GetOwnerAddress)(updateContract)(calcAdd)(const_calcAdd)(makeSum))接口说明:#
- init:初始化owner,owner地址即合约的部署者;
- 代理管理接口:
- RegisterProxy:注册代理合约地址,在业务合约1中没有对调用者进行限制,这会带来安全隐患;
- updateContract:向代理合约申请地址变更请求,将业务合约转移至其他的业务合约,这是合约在线更新的一个重要机制。接口执行成功后,本合约不再被代理,在业务合约1中,没有对本地保存的代理地址进行清理,这也会带来一定的安全隐患;
- 业务功能接口:
- calcAdd、const_calcAdd、makeSum,执行实际的业务操作。在业务合约1中,没有对调用者进行限制,这也会带来安全隐患。
业务合约2(calcContract)#
业务合约2完成实际的业务操作,同时也需要实现一定的代理管理操作功能。业务合约2采用了较为规范的实现方式,其业务接口只能通过代理进行访问。合约代码如下:
#include <platon/platon.hpp>#include <string>#include <vector>
CONTRACT calc_contract2 : public platon::Contract{public: ACTION void init(){ //the owner of the contract is best to be the operator of the deployment //in this instance, owner address can not be changed _ownerAddr.self() = std::pair<platon::Address, bool>(platon::platon_caller(), true);
//init the proxy _proxyAddr.self() = std::pair<platon::Address, bool>(platon::Address(), false); }
//this methods shall be called only after the proxy contract is deployed ACTION bool RegisterProxy(const std::string& proxyAddr){ //only owner can Register Proxy auto send_Addr = platon::platon_caller(); if (_ownerAddr.self().first != send_Addr){ return false; }
//set and register the proxy address auto p_Addr = platon::make_address(proxyAddr); if (!p_Addr.second){ _proxyAddr.self() = std::pair<platon::Address, bool>(platon::Address(), false); platon::internal::platon_throw("register proxy failed! illegal proxy address!"); return false; } else{ _proxyAddr.self() = p_Addr; return true; } }
CONST std::string GetProxyAddress(){ if (_proxyAddr.self().second){ return _proxyAddr.self().first.toString(); } else { return "proxy not initialized!"; } }
CONST std::string GetOwnerAddress(){ return _ownerAddr.self().first.toString(); }
//methods for proxy mechanism //the param is the next contract address the proxy really use ACTION bool updateContract(const std::string& contractAddr){ //only owner can updateContract auto send_Addr = platon::platon_caller(); if (_ownerAddr.self().first != send_Addr){ return false; }
//check the contract address auto c_Addr = platon::make_address(contractAddr); if (!c_Addr.second){ return false; }
//call proxy if (!_proxyAddr.self().second){ return false; }
auto result = platon::platon_call_with_return_value<bool>(_proxyAddr.self().first, (unsigned int)(0), (unsigned int)(0), "RegisterContract", contractAddr);
if (!result.second){ return false; }
//clear the proxy address _proxyAddr.self() = std::pair<platon::Address, bool>(platon::Address(), false); return result.second; }
//calculation methods, the interface must be the same with the proxy ACTION int calcAdd(int a, int b){ if (!_proxyAddr.self().second){ return -999999; }
//only proxy could call auto send_Addr = platon::platon_caller(); if (_proxyAddr.self().first != send_Addr){ return -999999; }
//be different with contract1 return a + b + 1000000; }
CONST int const_calcAdd(int a, int b){ if (!_proxyAddr.self().second){ return -999999; }
//only proxy could call auto send_Addr = platon::platon_caller(); if (_proxyAddr.self().first != send_Addr){ return -999999; } return a + b + 1000000; }
ACTION int makeSum(std::vector<int>& eles){ if (!_proxyAddr.self().second){ return -999999; }
//only proxy could call auto send_Addr = platon::platon_caller(); if (_proxyAddr.self().first != send_Addr){ return -999999; }
int rst = 0; for (auto itr = eles.begin(); itr != eles.end(); ++itr){ rst += *itr; } //be different with contract1 return rst + 1000000; }
private: //contracts using proxy mechanism are needed to using owner address principle. platon::StorageType<"owner"_n, std::pair<platon::Address, bool>> _ownerAddr; platon::StorageType<"proxy"_n, std::pair<platon::Address, bool>> _proxyAddr;};
PLATON_DISPATCH(calc_contract2, (init)(RegisterProxy)(GetProxyAddress)(GetOwnerAddress)(updateContract)(calcAdd)(const_calcAdd)(makeSum))接口说明:#
- init:初始化owner,owner地址即合约的部署者;
- 代理管理接口:
- RegisterProxy:注册代理合约地址,在业务合约2中对调用者进行了限制,只有合约owner(部署者)有权限调用,这是一种应对业务合约1中安全隐患的方式;
- updateContract:在业务合约2中,变更申请执行成功后,会对本地管理的代理进行清理,这是一种应对业务合约1中安全隐患的方式;
- 业务功能接口:
- calcAdd、const_calcAdd、makeSum,执行实际的业务操作。在业务合约2中,对调用者身份进行了限制,只有代理合约能够调用这些业务功能接口,即该合约的调用只能通过代理合约完成,这是一种应对业务合约1中安全隐患的方式,也是支持合约在线升级更新的一个重要机制;
- 业务合约2对每个计算结果,加了1000000,这是为了与合约1进行区分。
合约代理机制的运行机制#
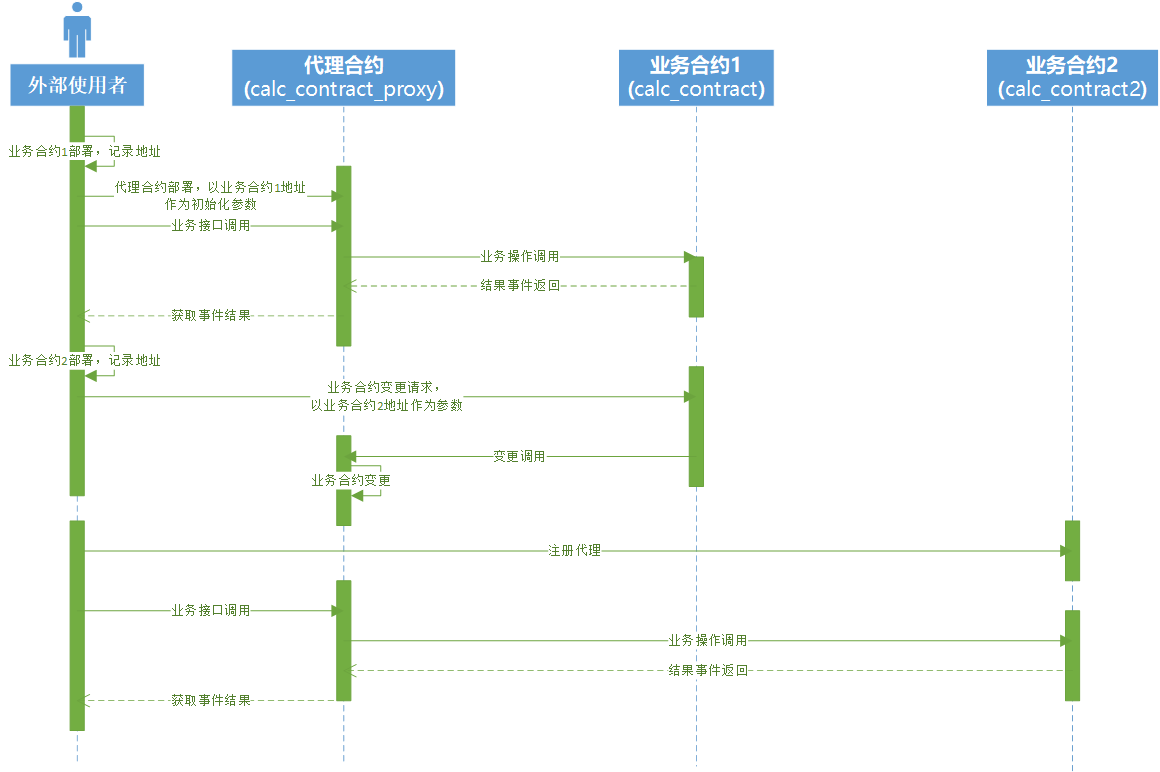
合约部署#
从代理合约、业务合约的初始化接口可以看出,合约的部署有一定的推荐顺序(非强制)。由于代理合约的部署需要输入一个合约地址(一般是被代理的业务合约的地址,也可以是普通地址),因此代理合约一般在业务合约完成部署后,才进行部署(以业务合约地址作为参数)。 如果代理合约部署时使用了普通的地址,则后续代理合约实际进行业务代理时,需要通过部署时传入的普通地址,调用代理合约的RegisterContract,来注册更新业务合约的地址,此后更新地址需要通过注册成功的合约来调用完成。 合约部署的操作方法在PlatON官网、前面的系列文章中已经有了详细的阐述,详见官方wasm合约开发手册:https://devdocs.platon.network/docs/zh-CN/Wasm_Dev_Manual/,以及《PlatON上的WASM智能合约开发(1)——合约开发入门》。
访问示例#
在本文示例中,首先使用platon-truffle工具部署了业务合约1,然后利用该合约地址部署代理合约。 代理机制的访问调用基于client-sdk-python开发,在测试使用中如果遇到问题,请通过下方二维码联系cross技术团队。 访问示例的完整代码如下:
from client_sdk_python import Web3, HTTPProvider, WebsocketProviderfrom client_sdk_python.eth import PlatON
true = Truefalse = Falsefrom_address = '...'
proxyAddr = '...'proxy_abi = []
contractAddr = '...'contract_abi = []
contractAddr_2 = '...'contract_2_abi = []
def proxyCall(): w3 = Web3(HTTPProvider("http://127.0.0.1:6789")) platon = PlatON(w3) hello = platon.wasmcontract(address=proxyAddr, abi=proxy_abi,vmtype=1)
tx_events_hash = hello.functions.calcAdd(73, 8).transact({'from':from_address,'gas':1500000}) tx_events_receipt = platon.waitForTransactionReceipt(tx_events_hash) rstAdd2 = hello.events.incalcAdd().processReceipt(tx_events_receipt) print('***********************calcAdd: ') print(rstAdd2)
tx_events_hash_sum = hello.functions.makeSum([11, 12, 13]).transact({'from':from_address,'gas':1500000}) tx_events_receipt_sum = platon.waitForTransactionReceipt(tx_events_hash_sum) rstAdd_sum = hello.events.inmakeSum().processReceipt(tx_events_receipt_sum) print('') print('***********************makeSum: ') print(rstAdd_sum[0]['args']['arg1']) return
def contract_1_Call(): w3 = Web3(HTTPProvider("http://127.0.0.1:6789")) platon = PlatON(w3)
hello = platon.wasmcontract(address=contractAddr, abi=contract_abi,vmtype=1) rstAdd = hello.functions.calcAdd(73, 8).call() print(rstAdd)
rstConst_Add = hello.functions.const_calcAdd(100, 99).call() print(rstConst_Add)
rstSum = hello.functions.makeSum([11, 12, 13]).call() print(rstSum) return
def contract_2_Call(): w3 = Web3(HTTPProvider("http://127.0.0.1:6789")) platon = PlatON(w3)
hello = platon.wasmcontract(address=contractAddr_2, abi=contract_2_abi,vmtype=1) rstAdd = hello.functions.calcAdd(73, 8).call() print(rstAdd)
rstConst_Add = hello.functions.const_calcAdd(100, 99).call() print(rstConst_Add)
rstSum = hello.functions.makeSum([11, 12, 13]).call() print(rstSum) return
def contract_1_to_2(): w3 = Web3(HTTPProvider("http://127.0.0.1:6789")) platon = PlatON(w3) hello = platon.wasmcontract(address=contractAddr, abi=contract_abi,vmtype=1)
print(hello.functions.GetOwnerAddress().call()) print(hello.functions.GetProxyAddress().call())
tx_events_hash = hello.functions.updateContract(contractAddr_2).transact({'from':from_address,'gas':1500000}) tx_events_receipt = platon.waitForTransactionReceipt(tx_events_hash) print(tx_events_receipt)
def c2_registerProxy(): w3 = Web3(HTTPProvider("http://127.0.0.1:6789")) platon = PlatON(w3) hello = platon.wasmcontract(address=contractAddr_2, abi=contract_2_abi,vmtype=1)
print(hello.functions.GetProxyAddress().call())
tx_events_hash = hello.functions.RegisterProxy(proxyAddr).transact({'from':from_address,'gas':1500000}) tx_events_receipt = platon.waitForTransactionReceipt(tx_events_hash) print(tx_events_receipt)
print(hello.functions.GetProxyAddress().call())
def contract_2_to_1(): w3 = Web3(HTTPProvider("http://127.0.0.1:6789")) platon = PlatON(w3) hello = platon.wasmcontract(address=contractAddr_2, abi=contract_2_abi,vmtype=1)
print(hello.functions.GetOwnerAddress().call()) print(hello.functions.GetProxyAddress().call())
tx_events_hash = hello.functions.updateContract(contractAddr).transact({'from':from_address,'gas':1500000}) tx_events_receipt = platon.waitForTransactionReceipt(tx_events_hash) print(tx_events_receipt)
def whichContract(): w3 = Web3(HTTPProvider("http://127.0.0.1:6789")) platon = PlatON(w3) hello = platon.wasmcontract(address=proxyAddr, abi=proxy_abi,vmtype=1)
rst = hello.functions.const_calcAdd(73, 8).call() print(rst)业务合约1#
业务合约1直接调用#
代码:
contract_1_Call()输出:
说明:
- 业务合约1中未作代理注册的限制,因此能直接执行操作。
代理调用业务合约1操作#
代码:
proxyCall()输出:
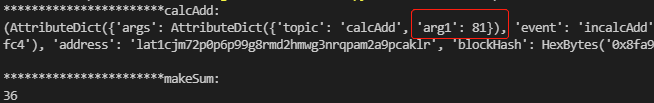
说明:
- 通过事件机制获取操作结果;
- 操作结果可在捕捉到的返回事件中,通过“rstAdd_sum[0]['args']['arg1']”来获取。
部署业务合约2#
使用platon-truffle工具部署业务合约2,获取其地址。
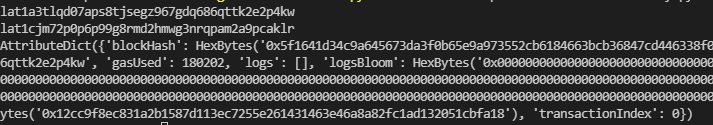
业务合约1,调用代理变更操作#
代码:
contract_1_to_2()输出:
业务合约2#
代理调用业务合约2操作#
此时,业务合约2尚未调用RegisterProxy进行代理注册。 代码:
proxyCall()输出:
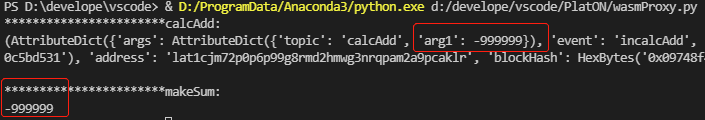
说明:
- 业务合约2中做了代理限制,在尚未注册代理时,无法完成正常的业务操作;
- 代理调用业务合约2虽然成功了,但是结果并非期望的值,这是一种在线更新的安全机制。
业务合约2注册代理#
代码:
c2_registerProxy()输出:
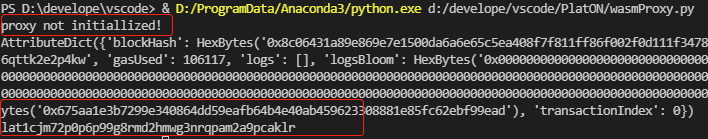
说明:
- 注册前后分别调用GetProxyAddress,观察当前管理的代理信息。
代理调用业务合约2操作#
代码:
proxyCall()输出:
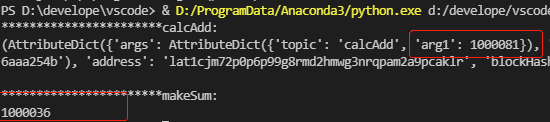
说明:
- 完成代理注册后,业务合约调用成功,返回期望结果。
业务合约2,调用代理变更操作#
代码:
contract_2_to_1()输出:
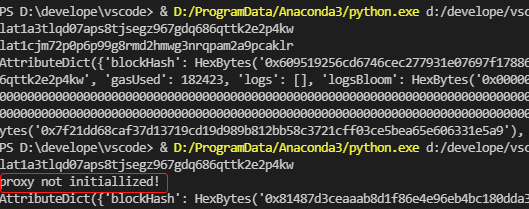
说明:
- 连续调用两次,第二次会发现业务合约2已经执行了代理信息清理工作。
本教程贡献者 @xiyu