PlaTrust Wallet
Preface#
Web3 is undoubtedly one of the hottest technology topics in recent years. The key to entering the Web3 world is a private key. However, for many users who are still using Web2, accustomed to logging in with account names and passwords, the concept of a private key can be a hurdle that prevents them from entering Web3. The long string of hexadecimal characters or random mnemonic phrases can be overwhelming. Another problem introduced by private keys is that losing the private key means losing access to assets in Web3, making secure storage of private keys a major concern. Additionally, as the ecosystem of public blockchains expands and more dapps emerge, gas fees have become higher, making it difficult for regular users to participate in Web3 activities due to the high transaction costs. Is there a wallet that allows users to access Web3 without the need to record private keys or mnemonic phrases (seedless) and without incurring huge transaction fees (gasless)? The answer lies in delegating the tasks to others. However, delegating ownership to others can lead to trust issues concerning one's assets in the Web3 world. In this scenario, a multi-signature contract wallet based on EIP-4337 perfectly addresses the pain points mentioned above.
Main use cases include:
- Companies and contracts can safely hold their funds and require the consent of a majority of owners to transfer funds. This way, no single owner can run away with the funds.
- Companies can execute sensitive transactions with the consensus of the majority of owners.
- Individuals can use multisig to have redundant keys. One feature of multisig is that if you lose one key, you can recover the wallet with the remaining two keys.
What is PlaTrust Wallet#
PlaTrust Wallet is a multi-signature contract wallet that follows the EIP-4337 specification. It lowers the barriers for Web2 users to enter Web3 and offers the following main features:
- Threshold-based Multisig: Manage assets in a multi-signature form based on the specified threshold.
- Session without Multi-Signature: Enable exemption from multi-signature operation within a specific time window to provide convenience for user wallet transactions.
- Wallet Lock: Allows wallet locking when owners suspect their account (device) has been compromised (lost, stolen, etc.).
- Custom Modules: Support user-defined modules that can be added to the wallet to introduce custom extensions.
- Wallet Recovery: Recover the wallet's ownership by replacing the lost private key with a new one through multi-signature initiated by other owners.
- Custom Role Control: Users can define different role information to control asset operation permissions in the wallet.
- Gasless: Users can operate the wallet without paying native tokens as gas fees.
- Wallet Upgrade: Upgrade the wallet to the latest version when new features or significant vulnerabilities arise.
- Account Whitelist: Set up a whitelist of accounts, allowing certain accounts to execute cross-account operations or transfers without considering trust issues.
- Censorship Resistance: Users have full control over their accounts without relying on any third-party services.
- Multi-chain Support: Compatible with all EVM-compatible public blockchains, ensuring the same wallet address across different EVM-compatible chains.
Feature Overview#
1. Threshold-based Multisig#
Explanation#
PlaTrust Wallet is a multi-signature contract wallet based on the EIP-4337 specification. It supports multiple owners and provides various wallet operations based on a multisig threshold. The concept of multisig is illustrated as follows:
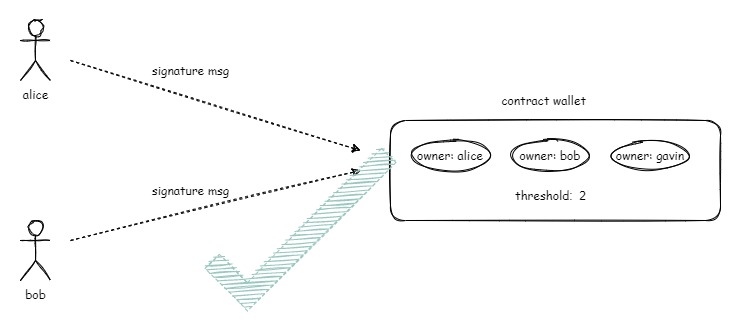
For each wallet operation (especially asset management), it must be signed by at least the threshold number of owners. Only when the required number of owner signatures is collected, the wallet operation can be successfully executed.
Functions and Use Cases#
- Maximizing Asset Protection when a Private Key is Lost: By holding multiple private keys, users can significantly reduce the risk of asset loss due to the loss or theft of a single private key. Even if one of the private keys is compromised, the funds will still be secure.
- Preventing Erroneous Transactions with Multiple Verifications: When a user initiates a transaction, other private key holders can prevent the execution of erroneous transactions by refusing to sign them. The more people involved in the verification process, the lower the possibility of erroneous transactions.
- Facilitating Collective Decision Making and Arbitration: When many co-signers jointly maintain the keys, fund control becomes more secure and organized. In this format, only unanimous decisions can be formed and executed, effectively implementing good decisions.
- Diversifying the Risk of Theft: By distributing keys across different geographical locations and multiple devices, users create a secure environment. Hackers will be unable to crack multiple distributed keys, thus keeping encrypted assets secure in the hands of users.
2. Session without Multi-Signature#
Explanation#
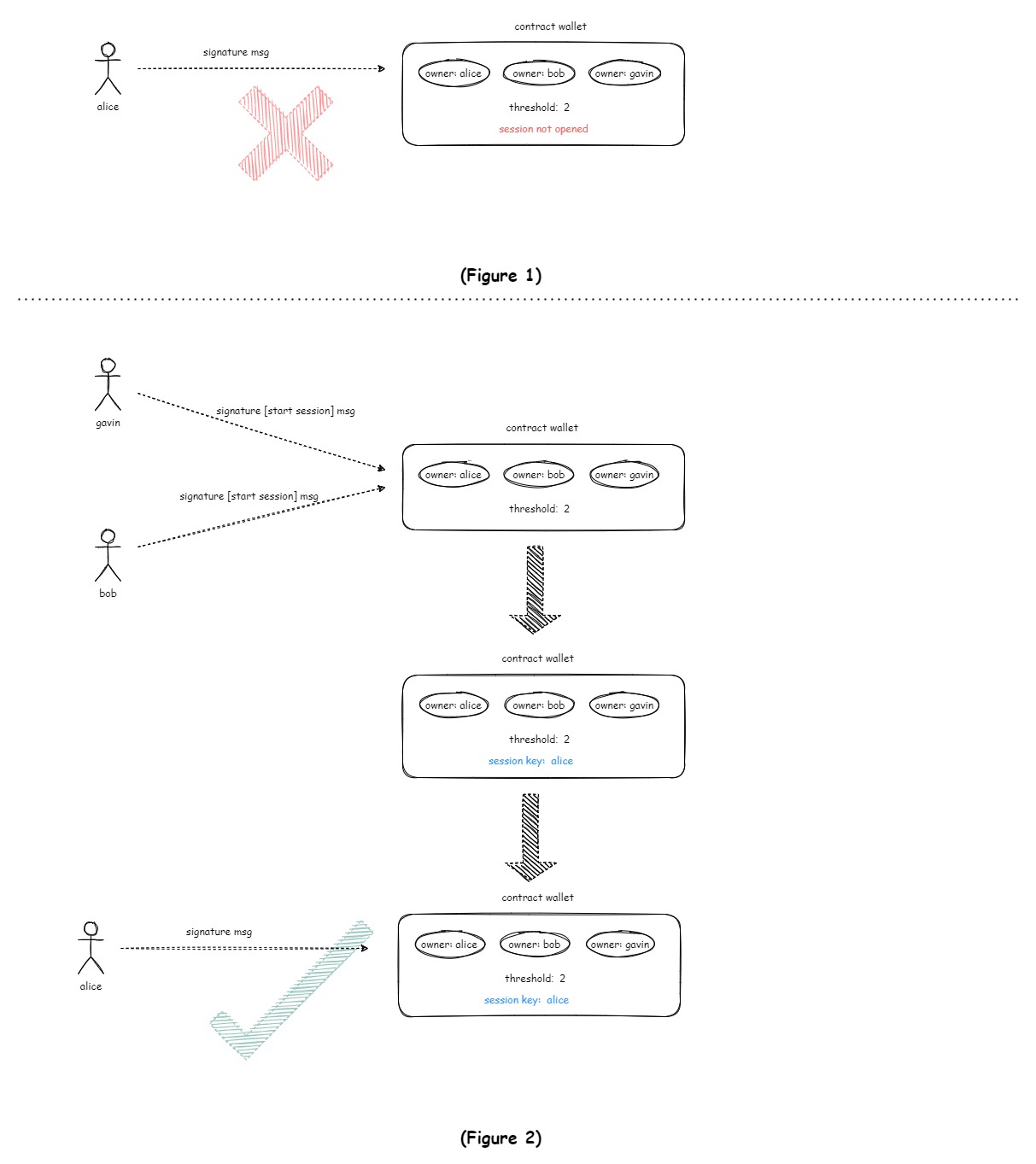
In certain scenarios, multisig introduces inconvenience for operations. Every time a wallet operation is performed, it requires signatures from the threshold number of owners to be effective. If a user wishes to perform numerous transactions within a specific time window and seeks to exempt from multisig and obtain permission from other owners, this can be achieved by creating a session without Multi-Signature. A session defines a temporary session key held by a specific owner, and as long as the session key is valid, the owner holding the session can use it to bypass multisig and execute any wallet call. The duration of the session is defined by the owner when creating it, and the session key will automatically expire at the end of the session.
Starting a session requires the number of signatures that satisfy the multisig threshold. The wallet's owners can close a session at any time before its expiration.
Functions and Use Cases#
- Providing Convenience for Operations within a Specific Time Window: During the valid time window, the holder of the session can operate the wallet without requiring other owners to participate in multisig.
- Uniqueness: Only one session can exist in the wallet at a given time window, and the session can only be held by the designated owner, with other owners not enjoying exemption from multisig calls.
- Expiration: Sessions have a specific time window of validity, and the session key will automatically expire after the validity period.
- Interruptible: During the session's validity period, the holder of the session can close the session without multisig, or other owners can close the session through multisig.
3. Wallet Lock#
Explanation#
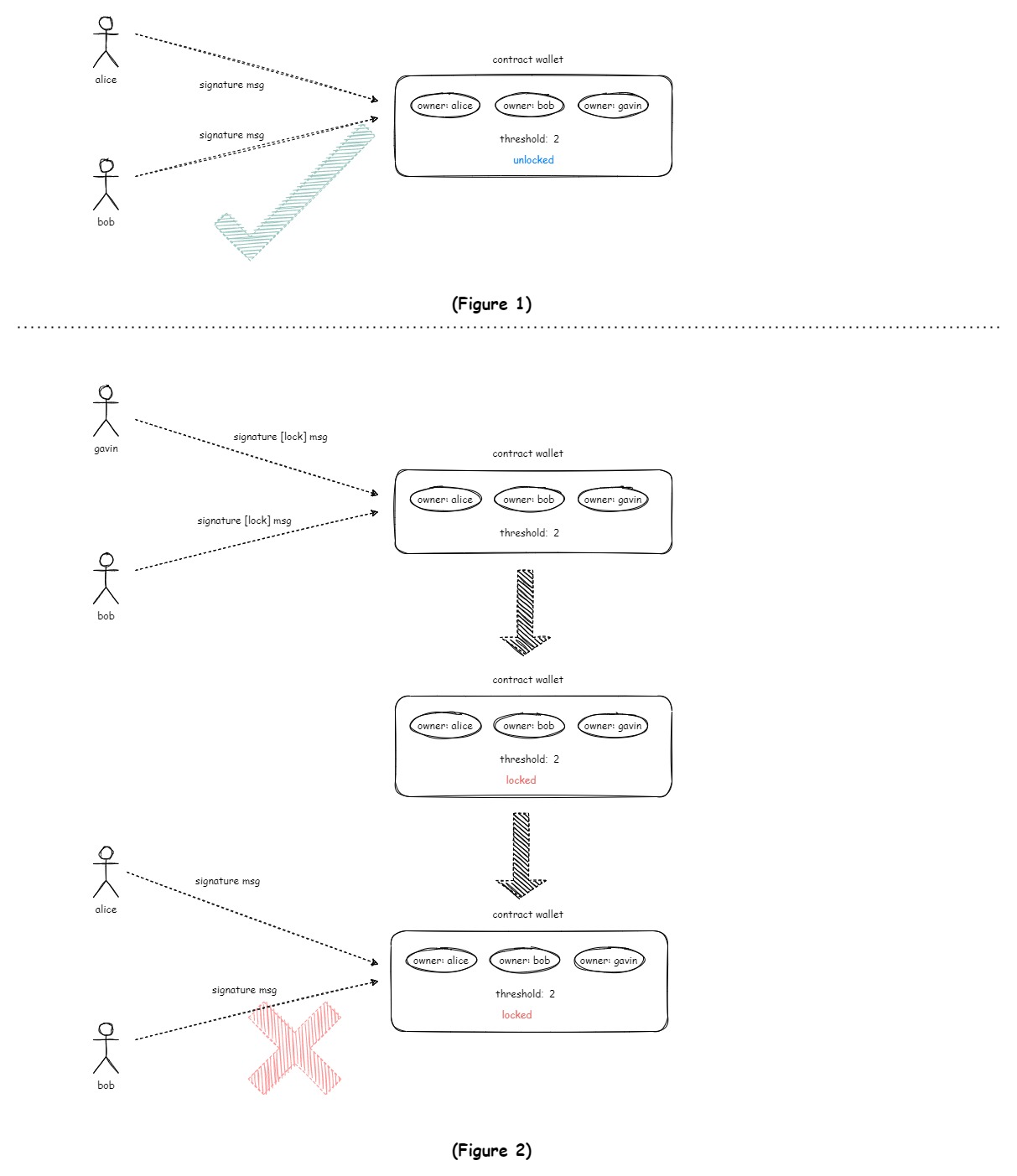
The wallet supports a lock feature, which allows owners to initiate a locking period when they suspect that their account (device) has been compromised (lost, stolen, etc.). During the wallet's locked period, only specific restricted operations, such as the unlock process, are allowed. All other operations (changing owners, changing multisig threshold, asset transfers, etc.) will be blocked.
To unlock the wallet before the security period ends, the owner needs to initiate a multisig unlock to trigger the wallet's unlocking.
Functions and Use Cases#
- Protecting Asset Security: When there is a suspicion of security issues with the wallet, it can be locked to prevent potential asset transfers.
- Limiting Wallet Operations: When the wallet is under attack, it can be locked to restrict wallet calls.
4. Custom Modules#
Explanation#
In PlaTrust Wallet, users can extend custom functional components to the wallet. By deploying custom module contracts and enabling them in the wallet through the "enable module" function, users can activate custom functional components for the wallet. Users can call functions from custom components and ultimately execute calls from the modules to the wallet using the executeFromModule function. It is important to note that each wallet contract instance will set the EIP-4337 entry contract RelayerManager as the default module during creation, and RelayerManager cannot be removed.
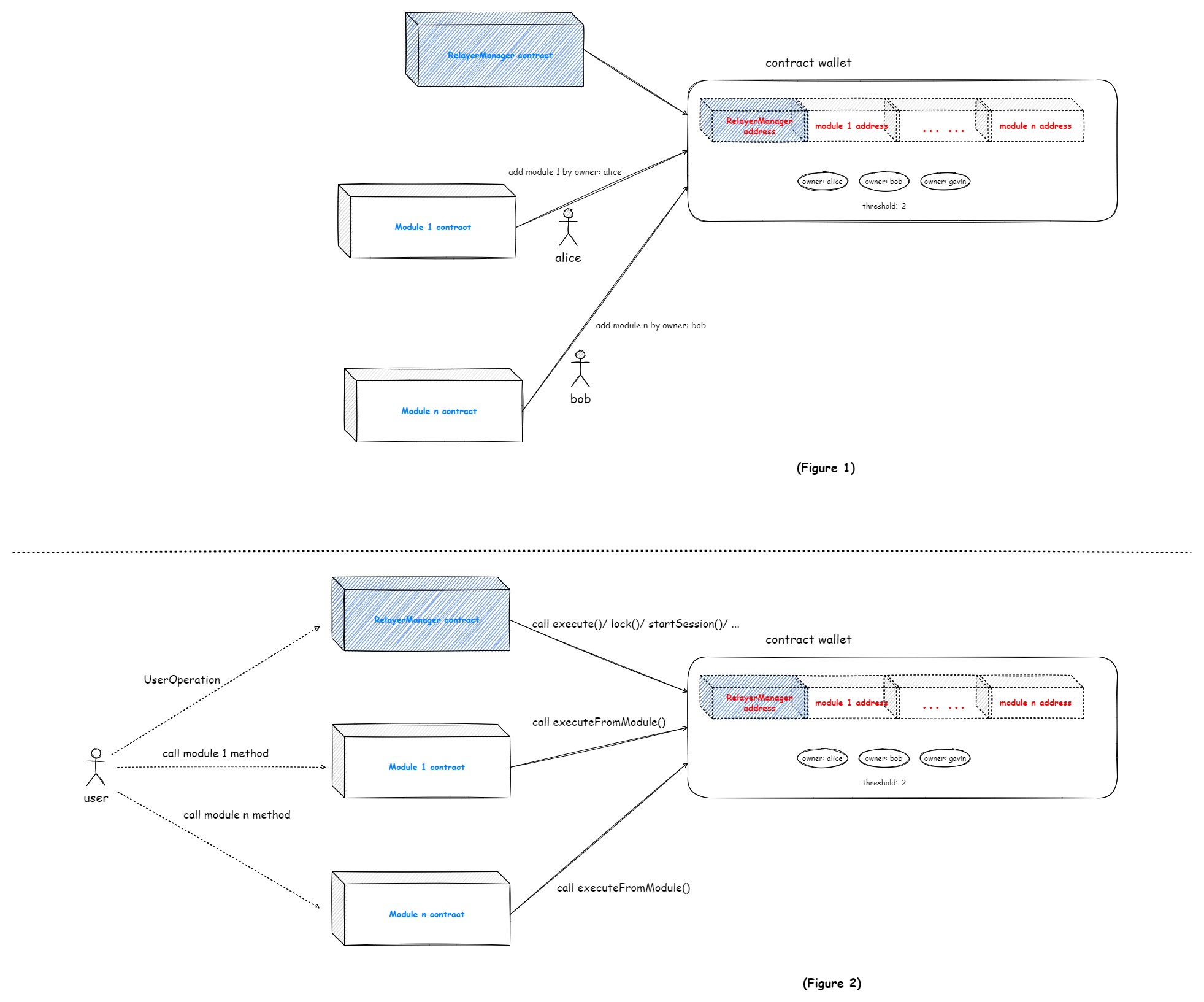
Functions and Use Cases#
- Scalability: Users can append custom functional components to their wallets, facilitating diverse extensions for the wallet.
- Plug-and-play: Apart from the built-in EIP-4337 entry contract RelayerManager, other custom modules can be freely enabled and disabled.
5. Wallet Recovery#
Explanation#
Ultimately, a contract wallet still requires an externally owned account (EOA) to perform operations. If the private key of the controlling contract owner is not properly saved, it can lead to a loss of the private key. When the control contract's owner's private key is lost, the user loses control of the wallet. To prevent this situation, the wallet includes a wallet recovery function. When an owner's private key is lost, the user can initiate the wallet recovery function to replace the old private key with a new one and regain control of the wallet. Changing to a new private key requires multisig from other owners in the wallet, and the number of signatures must meet the multisig threshold.
Functions and Use Cases#
- Preventing Users from Losing Access to the Wallet due to Lost Owner Private Keys.
6. Custom Role Control#
Explanation#
In many business scenarios, it is necessary to finely segment the functionality of a wallet based on different permissions, such as what admin users can do, what manager users can do, etc. Fine-grained functional permission has the advantage that different roles can perform different functions, ensuring each role fulfills its own responsibilities. In PlaTrust Wallet, users can add various custom roles and permissions, and specify the functions that can be called by each permission role, achieving fine-grained functional permission control.
Functions and Use Cases#
- Support for Fine-Grained Permission Control.
- Convenient for Managing and Extending Permissions.
7. Gasless#
Explanation#
PlaTrust Wallet is a multi-signature contract wallet based on EIP-4337, and the EIP-4337 standard natively supports "meta transactions." When owners of the wallet perform wallet-related functions, they assemble and sign what is called the "User Operation" message, then pass the User Operation to the relevant "Bundler" service for assembling and submitting the User Operation as a blockchain transaction. For wallet owners, they only need to sign the User Operation message with their corresponding owner private keys, without sending actual blockchain transactions. Hence, they do not need to pay any gas fees. For the Bundler service, upon receiving the User Operation and collecting the required multisig signatures, it assembles the User Operation and multisig signatures into a blockchain transaction and submits it to the chain, thereby incurring gas fees. The gas fees advanced by the Bundler are either covered by the tokens held by the wallet itself or filled in by the paymaster. Therefore, for wallet users (owners), PlaTrust Wallet exhibits gasless characteristics.
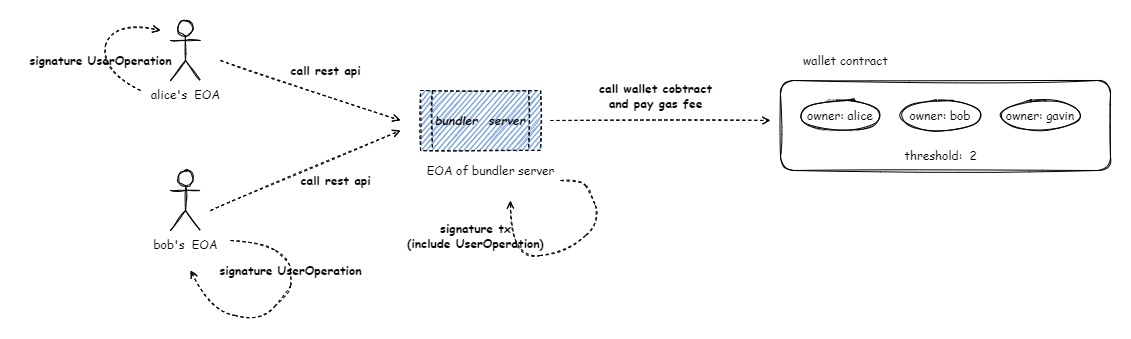
Functions and Use Cases#
- Allows users to continue using the wallet without being affected by gas fees when gas fees are becoming increasingly high.
- Promotes fair extraction of MEV (Miner Extractable Value) and encourages the community to join the construction of layer 2 solutions, especially for operators maintaining the bundler.
- Reduces barriers for Web2 users to use wallets.
8. Wallet Upgrade#
Explanation#
The contract wallet itself is a smart contract written by humans, and code written by humans can potentially have vulnerabilities. Once the smart contract is deployed to the chain, it becomes transparent to all users and cannot be easily modified or revoked. Thus, when encountering significant security vulnerabilities or malicious attacks, an upgrade is necessary to fix the flaws. For users, the on-chain address of the wallet remains the same, but the functions have been switched to the logic after the upgrade.
Functions and Use Cases#
- Flexibility in Functionality Changes.
- Ability to Fix Security Vulnerabilities.
9. Account Whitelist#
Explanation#
The whitelist of the wallet is designed to facilitate business usage and provide convenience for users based on a certain level of trust. The whitelist is further divided into dapp whitelist and account whitelist. Contracts addresses added to the dapp whitelist can be directly called with trust. Similarly, account whitelist addresses can directly perform transfer operations.
Functions and Use Cases#
- Increased Convenience.
- Based on Trust Premise.
10. Censorship Resistance#
Users can directly connect the functionality of the wallet to their own applications through the SDK, without relying on any third parties, and can directly use their own wallets.
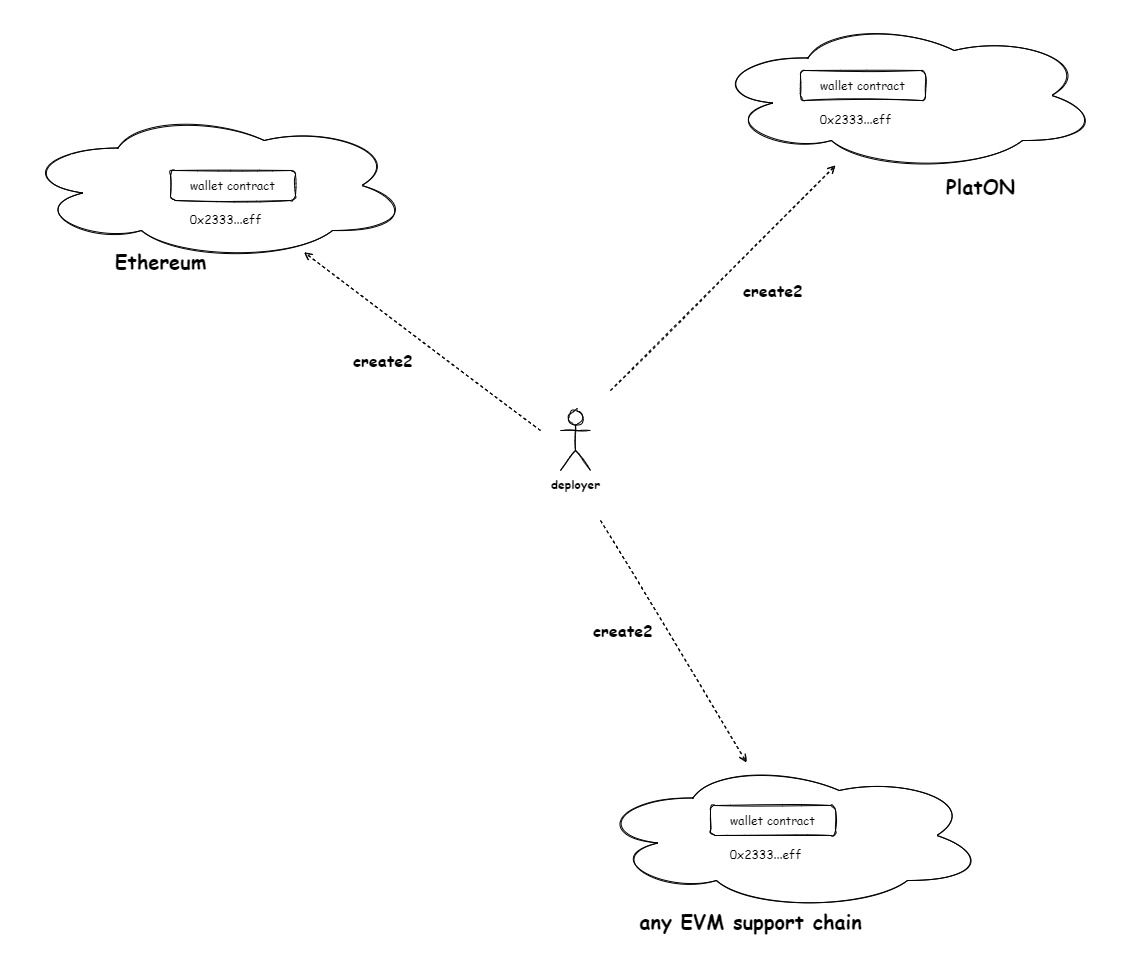
11. Multi-chain Support#
The wallet is deployed using the create2 opcode, which allows for the creation of the same contract address (also called a "counterfactual address") based on the same input parameters. This has the advantage that the wallet address can be known before the wallet contract is actually deployed on various EVM-compatible blockchains, allowing early funding of the wallet. Additionally, in many cross-chain projects, having the same contract address on multiple different blockchains facilitates wallet account management across different chains.